| Best
Uses of Air-
Keeping Warm, Keeping Cool.
Communicating and teaching insulation and ventilation - thermal barriers and bridges; convection, advection and conduction. |
|||||
|
Air has two important thermal properties: We can use these properties to maximise our personal
comfort levels with minimal disruption to the environment. Teaching Best Uses of Air -The
Challenge: Air and low frequency radiation (infrared radiation) have one great thing in common. We
cannot see them but we can feel them. We feel air as pressure. We feel
low frequency radiation as heat or the transfer of thermal energy.
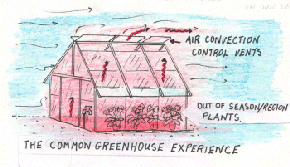
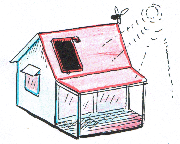
The Greenhouse Education Model
for communicating and
teaching
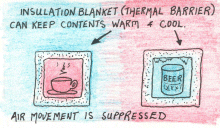
Insulation
(Building and Clothing). We place great value on sensory data derived from tactile
experiences and greenhouses present us with a vital ‘window of
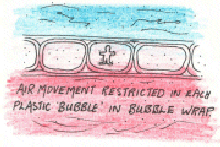
opportunity’ to know the invisible. This is because greenhouses offer unique opportunities to experience the controlled suppression of convection and advection.
Students can
immerse themselves in a human designed and controlled microclimate and
have these concurrent, cumulative experiences:
This immersion experience can be extended and linked to a range of common insulation experiences:
Effective use of air can enhance personal comfort levels
while conserving these resources for future generations.
|
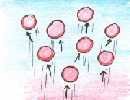
Symbol of infrared radiation
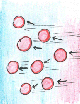
Convection
= upward movement of air mass. Advection = horizontal movement of air mass.
|
||||